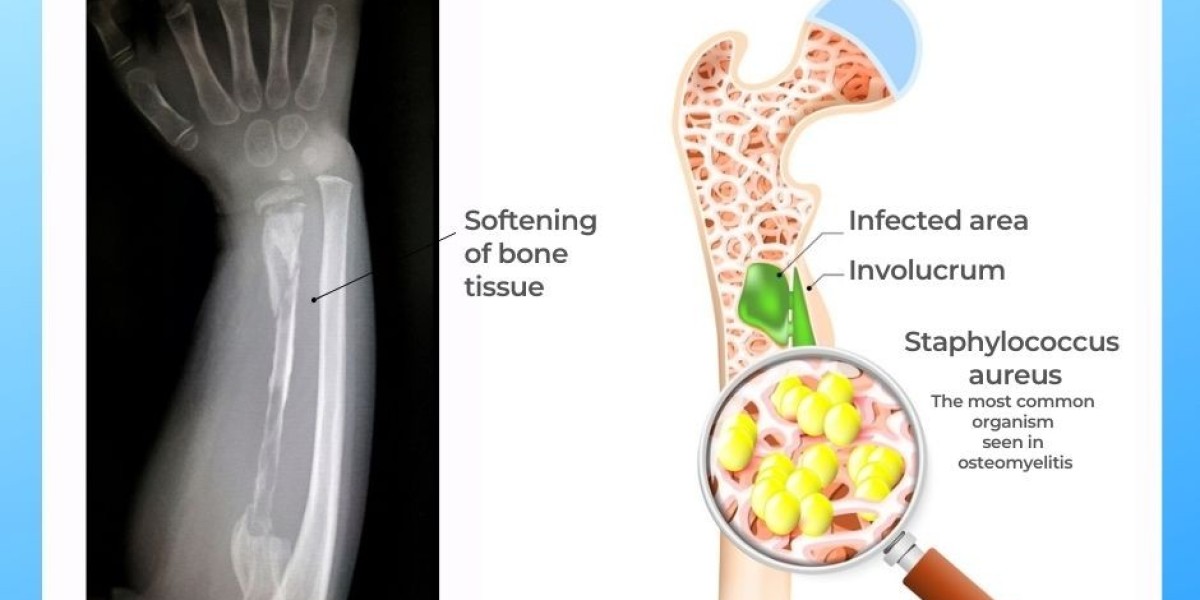
Osteomyelitis treatment, an infection of the bone, is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to prevent complications such as bone damage or chronic infection. Here’s an overview of the most commonly used approaches to treat osteomyelitis.
1. Diagnosis
Before treatment begins, an accurate diagnosis is essential. This typically involves:
- Blood Tests: Detect markers of infection such as elevated white blood cells and inflammatory markers.
- Imaging: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to identify bone damage or abscesses.
- Biopsy: A bone sample may be taken to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for osteomyelitis.
- Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics: These are often administered for 4–6 weeks to address acute infections.
- Oral Antibiotics: After initial IV therapy, oral antibiotics may be prescribed for several weeks or months.
- Tailored Treatment: The choice of antibiotics depends on the type of bacteria or fungi identified in the bone biopsy.
3. Surgical Intervention
In cases where the infection is severe or antibiotics are insufficient, surgery may be necessary.
- Debridement: Removing infected bone tissue and surrounding material to prevent the spread of infection.
- Abscess Drainage: Draining any pus-filled areas near the bone.
- Bone Grafting: Replacing removed bone with graft material to support healing.
- Amputation (Rare Cases): In extreme situations, the affected limb may be removed to save the patient’s life.
4. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
HBOT is sometimes used as an adjunct treatment, particularly in chronic osteomyelitis.
- How It Works: The patient breathes pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which enhances oxygen delivery to tissues, promoting healing and combating infection.
5. Pain Management
Managing pain is an important aspect of osteomyelitis treatment.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, or prescription pain medications in severe cases.
- Physical Therapy: Helps improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
6. Long-Term Care and Monitoring
Patients with osteomyelitis require careful monitoring to ensure the infection doesn’t recur.
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups to track recovery progress.
- Imaging Studies: Periodic imaging may be needed to confirm healing.
- Rehabilitation: For patients who undergo surgery, physical therapy helps regain function and strength.
7. Prevention
Preventing osteomyelitis involves reducing risk factors:
- Infection Control: Promptly treat cuts, wounds, and infections.
- Chronic Condition Management: Keep diabetes and other chronic illnesses well-controlled.
- Surgical Precautions: Ensure proper sterilization during surgical procedures.
Prognosis
With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most cases of osteomyelitis can be effectively managed. Chronic cases may require extended care but are often treatable with a multidisciplinary approach.
If you suspect osteomyelitis, consult a healthcare provider immediately for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
Naijamatta is a social networking site,
download Naijamatta from Google play store or visit www.naijamatta.com to register. You can post, comment, do voice and video call, join and open group, go live etc. Join Naijamatta family, the Green app.
Click To Download