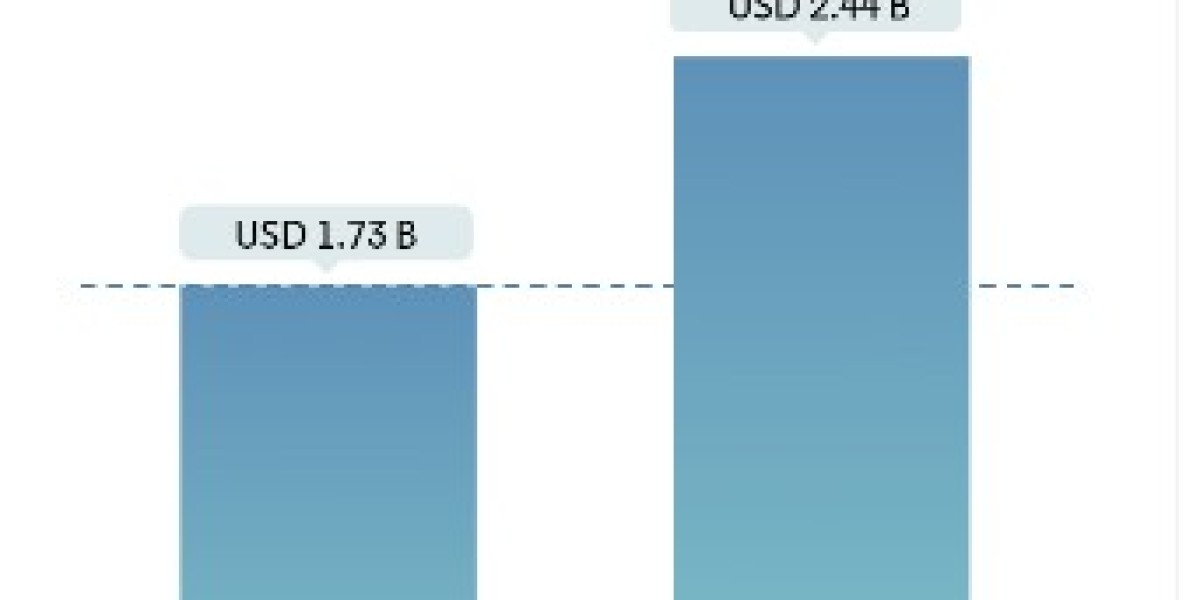
Market Overview:
Japan, with its aging population and high prevalence of diabetes, presents a significant market for diabetes care devices. The country has seen an increasing demand for advanced devices to manage diabetes, driven by the growing number of diabetic patients and a shift towards more personalized, efficient care solutions. Japan's healthcare infrastructure is highly developed, and the country’s emphasis on technological advancements and healthcare innovation further supports the growth of the diabetes devices market. From glucose monitoring systems to insulin delivery devices, Japan is a key player in the diabetes care sector, offering a wide range of products designed to improve patient outcomes and convenience.
Key Trends:
Increasing Diabetes Prevalence:
Japan's aging population is a major contributor to the rising incidence of diabetes. As the elderly population grows, the demand for diabetes management solutions, including devices for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin delivery, continues to rise.
Technological Advancements in Diabetes Care:
The Japan diabetes devices market is witnessing rapid advancements, particularly in glucose monitoring systems. Innovations such as non-invasive glucose monitoring devices and connected systems that provide real-time data are transforming diabetes management.
Rise in Demand for Wearable Diabetes Devices:
Wearable devices such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps are gaining popularity due to their ability to offer real-time monitoring and seamless integration into the user's daily life. These devices are improving diabetes management, allowing for more flexibility and precision in treatment.
Shift Toward Personalized Diabetes Care:
There is a growing trend toward personalized diabetes management. The integration of diabetes devices with digital health platforms and mobile applications allows for more tailored treatment plans, enabling patients to track and manage their condition more effectively.
Government Initiatives and Healthcare Reforms:
The Japanese government is increasingly supporting diabetes management through healthcare reforms and policies aimed at improving accessibility to diabetes care devices. Initiatives promoting early detection and continuous care are expected to drive market growth.
Challenges:
High Costs of Advanced Devices:
The cost of advanced diabetes care devices, such as insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems, can be prohibitive for some patients, particularly in a country where healthcare expenses are a concern. Despite technological advancements, the affordability of these devices remains a challenge.
Regulatory Hurdles:
Regulatory approval for new diabetes devices can be a lengthy and complex process in Japan. This poses a challenge for companies looking to enter the market with innovative products, as they must navigate strict standards and regulations set by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW).
Market Saturation in Urban Areas:
While there is substantial demand for diabetes care devices in Japan’s urban centers, the market is becoming increasingly saturated. The challenge lies in reaching rural populations where healthcare access may be limited, and patients may have less awareness of new diabetes management technologies.
Need for Consumer Education:
Although there is growing awareness of diabetes, many consumers remain uninformed about the latest diabetes care technologies. Companies in the market need to invest in consumer education to encourage the adoption of newer, more advanced devices.
Conclusion:
Japan's diabetes devices market is experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging population, increasing diabetes prevalence, and technological innovations. As the demand for personalized and wearable diabetes management devices rises, companies are introducing advanced solutions to improve patient outcomes. However, challenges such as high costs, regulatory hurdles, and market saturation in urban areas remain. To continue thriving, the industry must focus on improving device affordability, increasing consumer education, and expanding access to rural areas. With the right strategies, the Japanese diabetes devices market has a promising future ahead.
Naijamatta is a social networking site,
download Naijamatta from Google play store or visit www.naijamatta.com to register. You can post, comment, do voice and video call, join and open group, go live etc. Join Naijamatta family, the Green app.
Click To Download