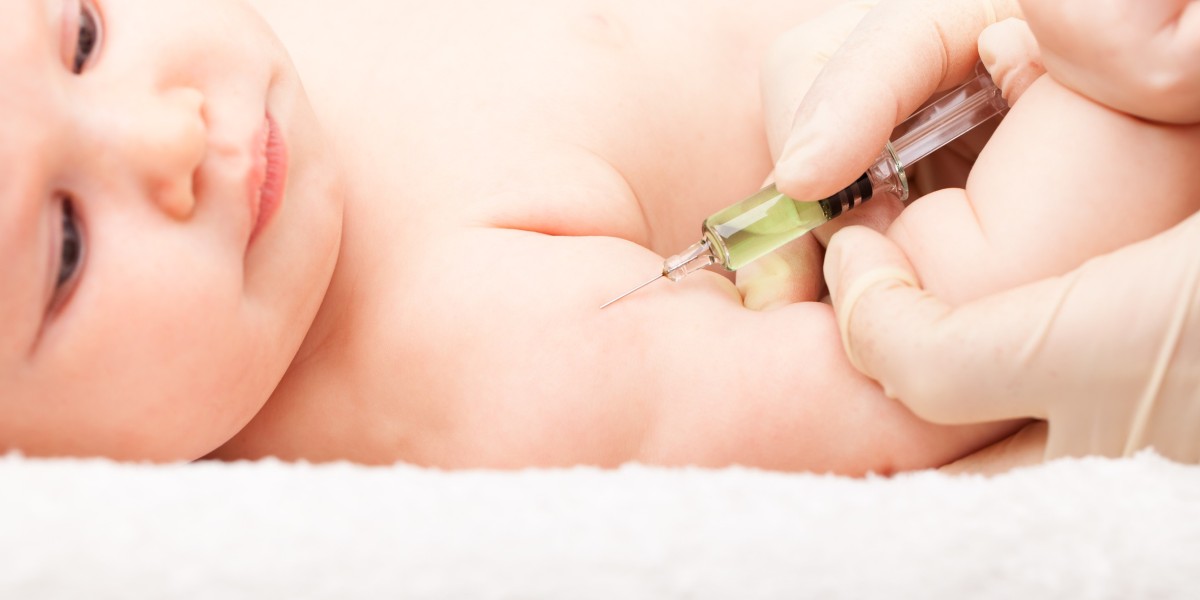
The development of vaccines has played a huge role in improving child health outcomes over the past century. Some of the earliest pediatric vaccines targeted diseases like smallpox and rabies which have been around for thousands of years. In the late 1700s, English physician Edward Jenner developed one of the first successful vaccines - for smallpox. He discovered that infection from cowpox afforded protection against smallpox in humans. Over the following decades, vaccination programs helped eradicate smallpox worldwide by 1980.
In the early 1900s, other important childhood vaccines were created such as those for diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus. French scientists created the first combined DPT vaccine in the 1920s. The polio vaccine was developed in the 1950s by Jonas Salk and greatly reduced the prevalence of paralytic polio in industrialized nations. Measles, mumps and rubella vaccines became available in the 1960s, helping to control outbreaks of these highly contagious diseases. Continued research led to new combination vaccines that allowed multiple diseases to be protected against with fewer shots.
Pediatric Vaccine Workings
Pediatric Vaccines work by priming the immune system with something that resembles a pathogen like a virus or bacteria. This causes the body to develop antibodies and memory cells that will recognize and fight off the actual pathogen if exposed to it later on. Most vaccines contain an inactivated or weakened version of the germ that causes a disease. Some contain just pieces of the germ like its proteins or toxins.
When the vaccine is administered, the immune system recognizes that the antigens do not belong in the body. It produces antibodies that will remain for years, providing protection. If exposure happens later, these memory cells can rapidly manufacture more antibodies to destroy the pathogen before disease develops. Vaccines are tested rigorously for safety and ability to produce an immune response before approval for public use.
Benefits of Pediatric Vaccination Programs
Widespread childhood vaccination programs have dramatically reduced morbidity and mortality from vaccine-preventable diseases. Prior to vaccines, diseases like measles, pertussis and polio threatened the lives of millions of children globally each year. According to the WHO and CDC, vaccination prevents an estimated 2-3 million deaths worldwide annually.
In the United States, vaccination has led to the eradication of smallpox and elimination of many other diseases from circulation. Diseases that were once very common like Haemophilus influenza type b meningitis, measles and rubella are now rare thanks to effective immunization programs. This "herd immunity" protects those who cannot receive certain vaccines due to age or health conditions. The savings to the healthcare system and costs avoided from adverse events are substantial.
Some Key Recommended Childhood Vaccines
DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) - Provides protection against three serious bacterial infections.
Polio - Protects against the paralytic disease poliomyelitis which can cause permanent disability. OPV (oral) and IPV (inactivated) versions available.
MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) - Combined measles, mumps and rubella vaccine to prevent these highly contagious viral diseases.
Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) - Vaccine for Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteria which is a leading cause of meningitis in young children.
PCV13/PPSV23 (Pneumococcal) - Protects against pneumonia, bacteremia and meningitis from Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria in 13 and 23 serotypes.
Hepatitis B - Protects the liver from Hepatitis B virus which can cause acute and chronic disease.
Rotavirus - Oral vaccine for the most common cause of severe diarrhea among young children worldwide.
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) - Vaccine series protects females/males against cancers caused by HPV strains 16 and 18.
Influenza - Annual flu shot recommended for children 6 months and older to prevent seasonal flu.
Challenges and Addressing Hesitancy
As the number of recommended vaccines increased overtime due to new scientific discoveries, some parents began expressing concerns about the safety of the accelerated schedule. While severe reactions are rare, the perception that vaccines are unsafe due to unfounded claims linking them to autism is widespread in some communities. Lack of trust in health authorities has grown in recent years in many nations.
Public health officials have responded to hesitancy issues by improving education efforts around vaccine safety science. They emphasize the need to protect community immunity for vulnerable groups. Physicians play an important role addressing specific parental concerns in an understanding manner. Ongoing monitoring of vaccine safety helps restore confidence as problems are swiftly addressed when they do emerge post-licensure. Overcoming hesitancy requires ongoing effort from researchers, officials and community leaders alike to promote child wellness.
Pediatric vaccination programs are one of public health's greatest success stories. Continuous medical advances will lead to new and improved vaccines that prevent additional diseases. While challenges around hesitancy remain, ensuring high global vaccination coverage presents an opportunity improve child health worldwide. Through patient efforts to understand parental concerns and improve communication, we can work to eliminate vaccine-preventable illnesses altogether in future generations. Protecting children with safe, effective immunization is crucial for building a healthier society for all.
Get More Insights on- Pediatric Vaccines
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want:
About Author:
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement.
(LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)
Naijamatta is a social networking site,
download Naijamatta from Google play store or visit www.naijamatta.com to register. You can post, comment, do voice and video call, join and open group, go live etc. Join Naijamatta family, the Green app.
Click To Download